


Next: 10.1.1 Pass 1: Cross-Dispersion
Up: 10 High-Dispersion Flux Extraction
Previous: 10 High-Dispersion Flux Extraction
The determination of smoothed background fluxes is made using the
high-dispersion resampled image (SI). A representative high-dispersion
SI given in Figure 10.1 shows the echelle orders running
horizontally and the spatial (cross-dispersion) direction running
vertically. We will refer hereafter to the image sectors at the top and
bottom as the ``ends'' of the image. The background extraction module
(BCKGRD)
produces smoothed background flux spectra which,
together with the gross spectra, form the net spectra. The background
model is created by computing continuous Chebyshev polynomial functions
from
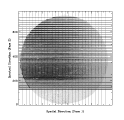 Figure 10.1:
Layout of the background extraction swaths on a
sample SWP high-dispersion image. Lines running in the vertical
(spatial) direction are the Pass 1 extractions. The reconstructed
background solutions created in Pass 2 are placed in the positions of
the echelle orders (horizontal lines).
Figure 10.1:
Layout of the background extraction swaths on a
sample SWP high-dispersion image. Lines running in the vertical
(spatial) direction are the Pass 1 extractions. The reconstructed
background solutions created in Pass 2 are placed in the positions of
the echelle orders (horizontal lines).
pixels that sample valid background fluxes. BCKGRD models the
backgrounds of images having continuum flux in two one-dimensional
passes. For images with no continuum, the algorithm proceeds
straightforwardly by sampling the neighboring interorder fluxes for each
spectral order and fitting the result to a Chebyshev polynomial. In the
sections below, the salient features of BCKGRD are described;
this process is presented in greater detail in Appendix A.



Next: 10.1.1 Pass 1: Cross-Dispersion
Up: 10 High-Dispersion Flux Extraction
Previous: 10 High-Dispersion Flux Extraction
Karen Levay
12/4/1997
 Figure 10.1:
Layout of the background extraction swaths on a
sample SWP high-dispersion image. Lines running in the vertical
(spatial) direction are the Pass 1 extractions. The reconstructed
background solutions created in Pass 2 are placed in the positions of
the echelle orders (horizontal lines).
Figure 10.1:
Layout of the background extraction swaths on a
sample SWP high-dispersion image. Lines running in the vertical
(spatial) direction are the Pass 1 extractions. The reconstructed
background solutions created in Pass 2 are placed in the positions of
the echelle orders (horizontal lines).