


Next: References
Up: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope:
Previous: Performance
The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope performed successfully aboard the Astro-1
space shuttle mission and obtained a large number of spectra bearing on
a wide range of astrophysical topics in its brief 9 day flight. Observations of the DA white dwarf G191-B2B have been used to derive a photometric calibration curve for HUT that is believed accurate to better than 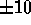 %. The data
obtained by HUT represent the first extensive spectrophotometric observations in the
912--1216 Å band to bridge the gap between the Copernicus spectroscopy of
bright stars at high resolution, and the Voyager observations at much
lower resolution. It is expected that improvements to the shuttle spacelab
systems, especially the IPS performance, together with a longer duration flight and a moderate improvement of the spectrograph efficiency, may enable HUT to obtain nearly an order-of-magnitude more data on the Astro-2 mission, now planned for launch in 1994.
%. The data
obtained by HUT represent the first extensive spectrophotometric observations in the
912--1216 Å band to bridge the gap between the Copernicus spectroscopy of
bright stars at high resolution, and the Voyager observations at much
lower resolution. It is expected that improvements to the shuttle spacelab
systems, especially the IPS performance, together with a longer duration flight and a moderate improvement of the spectrograph efficiency, may enable HUT to obtain nearly an order-of-magnitude more data on the Astro-2 mission, now planned for launch in 1994.
Acknowledgements
It is a pleasure to acknowledge the assistance of the staff at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in the design and development of HUT. These include K. Heffernan, B. Ballard, J. Hayes, L. Kohlenstein, and many others. We also thank H. Weaver and K. Chambers for their substantial contributions to the HUT instrument development. E. Mackey (Spacom), R. Crabbs (RSI), and V. Muffaletto also contributed significantly to the hardware development. We are grateful to all the NASA personnel who supported the Astro-1 mission, especially J. Jones and T. Gull, and the crew of STS-35. One of us (AFD) would particularly like to record his debt to William G. Fastie, who provided invaluable inspiration for this project at its inception.
The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope project is supported by NASA contract
NAS5-27000 to the Johns Hopkins University.
afd@pha.jhu.edu
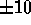 %. The data
obtained by HUT represent the first extensive spectrophotometric observations in the
912--1216 Å band to bridge the gap between the Copernicus spectroscopy of
bright stars at high resolution, and the Voyager observations at much
lower resolution. It is expected that improvements to the shuttle spacelab
systems, especially the IPS performance, together with a longer duration flight and a moderate improvement of the spectrograph efficiency, may enable HUT to obtain nearly an order-of-magnitude more data on the Astro-2 mission, now planned for launch in 1994.
%. The data
obtained by HUT represent the first extensive spectrophotometric observations in the
912--1216 Å band to bridge the gap between the Copernicus spectroscopy of
bright stars at high resolution, and the Voyager observations at much
lower resolution. It is expected that improvements to the shuttle spacelab
systems, especially the IPS performance, together with a longer duration flight and a moderate improvement of the spectrograph efficiency, may enable HUT to obtain nearly an order-of-magnitude more data on the Astro-2 mission, now planned for launch in 1994.


