|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
The MUSCLES and Mega-MUSCLES Treasury Surveys - Spectra of M & K Exoplanet Host Stars from the X-ray and Ultraviolet to the Infrared
| MUSCLES PI: Kevin France (Colorado) | |
| Mega-MUSCLES PI: Cynthia Froning (UT Austin) | |
| MUSCLES Series: | |
| MUSCLES Paper I - France et al. 2016, ApJ, 820, 89 | MUSCLES Paper IV - Youngblood et al. 2017, ApJ, 843, 31 |
| MUSCLES Paper II - Youngblood et al. 2016, ApJ, 824, 101 | MUSCLES Paper V - Loyd et al. 2018, ApJ, 867, 71L |
| MUSCLES Paper III - Loyd et al. 2016, ApJ, 824, 102 | Brown et al. 2023, AJ, 165, 195 |
| Mega-MUSCLES Series: | |
| Mega-MUSCLES Paper I - Froning et al. 2019, ApJ, 871L, 26F | Mega-MUSCLES Paper II - Wilson et al. 2021, ApJ, 911, 18W |
| France et al. 2020, AJ, 160, 237 | Linsky et al. 2020, ApJ, 902, 3 |
| MUSCLES Extension: | |
| Behr et al. 2023, AJ, 166, 35 | |
| Semi-Empirical Synthetic Models: | |
| Fontenla et al. 2016, ApJ, 830, 154 | Duvvuri et al. 2021, ApJ, 913, 40 |
| Tilipman et al. 2021, ApJ, 909, 61 | |
Introduction |
Data Products |
Data Access |
Plot Scripts |
README (TXT) |
| Acknowledgements:
MUSCLES: If you make use of the MUSCLES spectral data products, please cite Papers I, II, and III from the top of this page and specify the version number of the spectra you used in your work. The version number is in the filenames. For example, "v22" denotes version 2.2. Mega-MUSCLES: If the spectral data products are from the Mega-MUSCLES survey (which have versions of "v23" and are denoted by a double asterisk ** in the Data Access table), please cite Mega-MUSCLE Paper II from the top of this page. MUSCLES Extension: If the spectral data products are from the MUSCLES Extension survey (which have versions of "v24"), please cite the MUSCLES Extension paper from the top of this page. Synthetic Models:If you use the semi-empirical synthetic models, please cite the relevant paper(s) in the "Semi-Empirical Synthetic Models" section at the top of the page. |
||||
Introduction
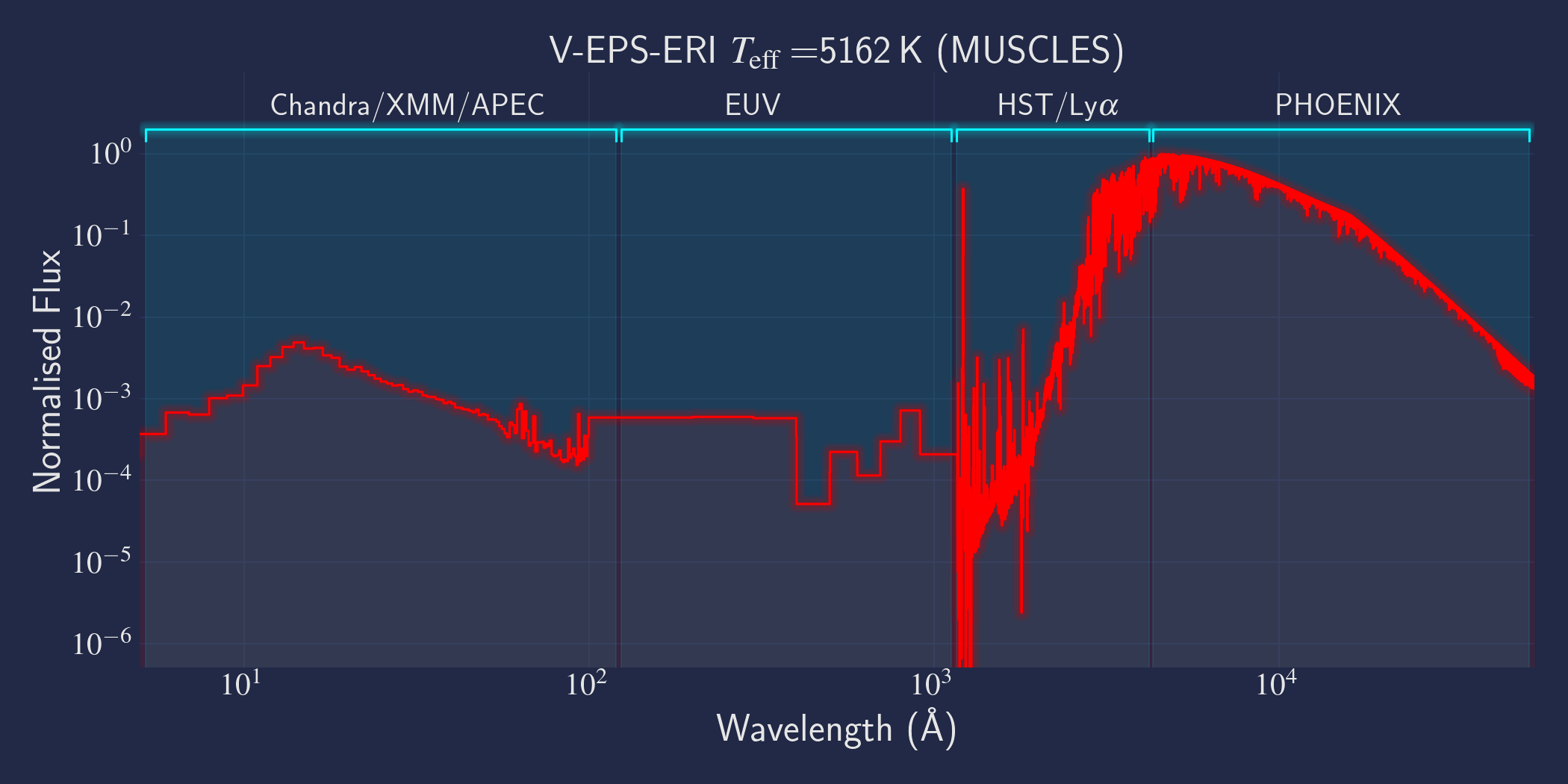
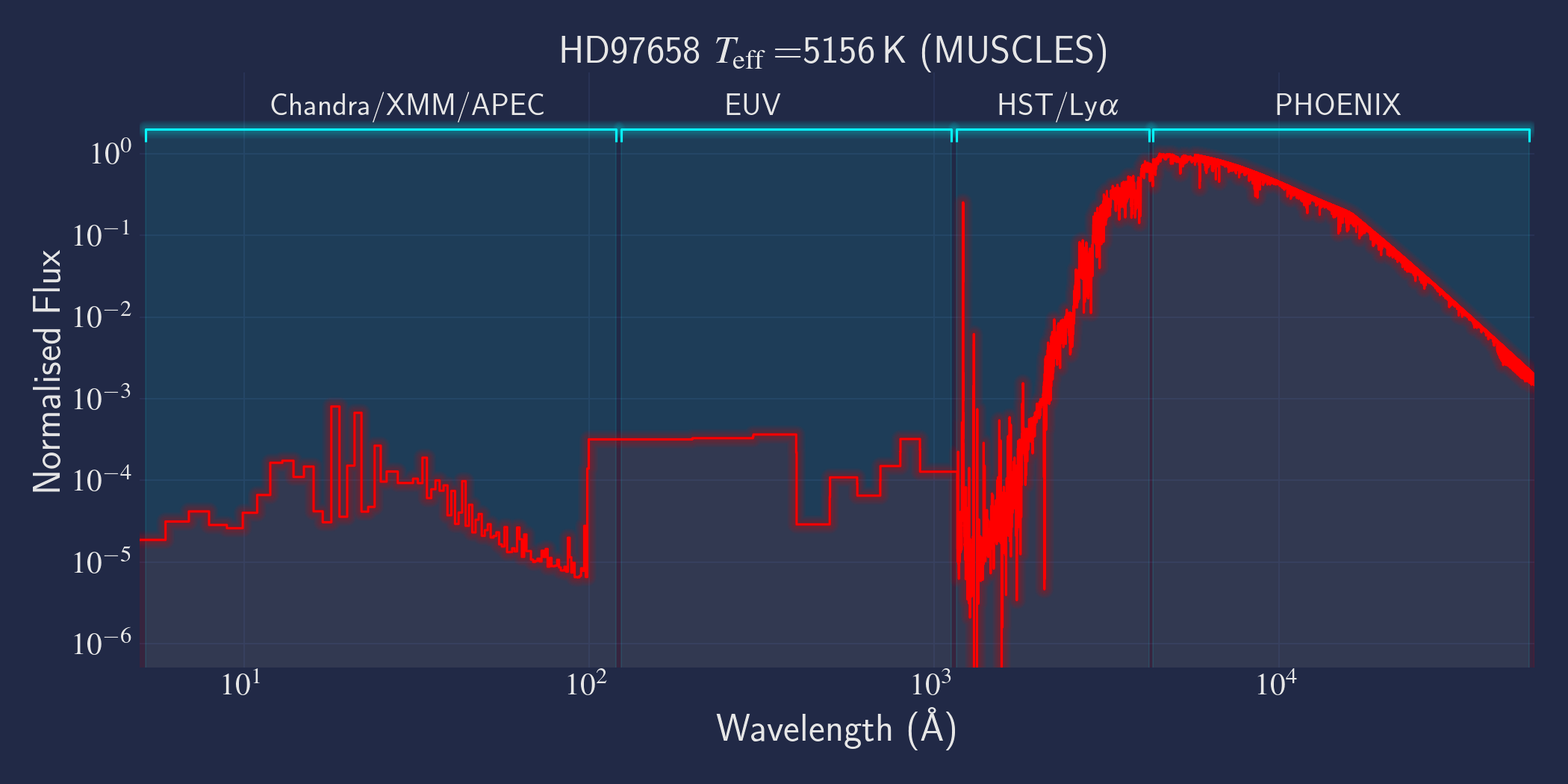
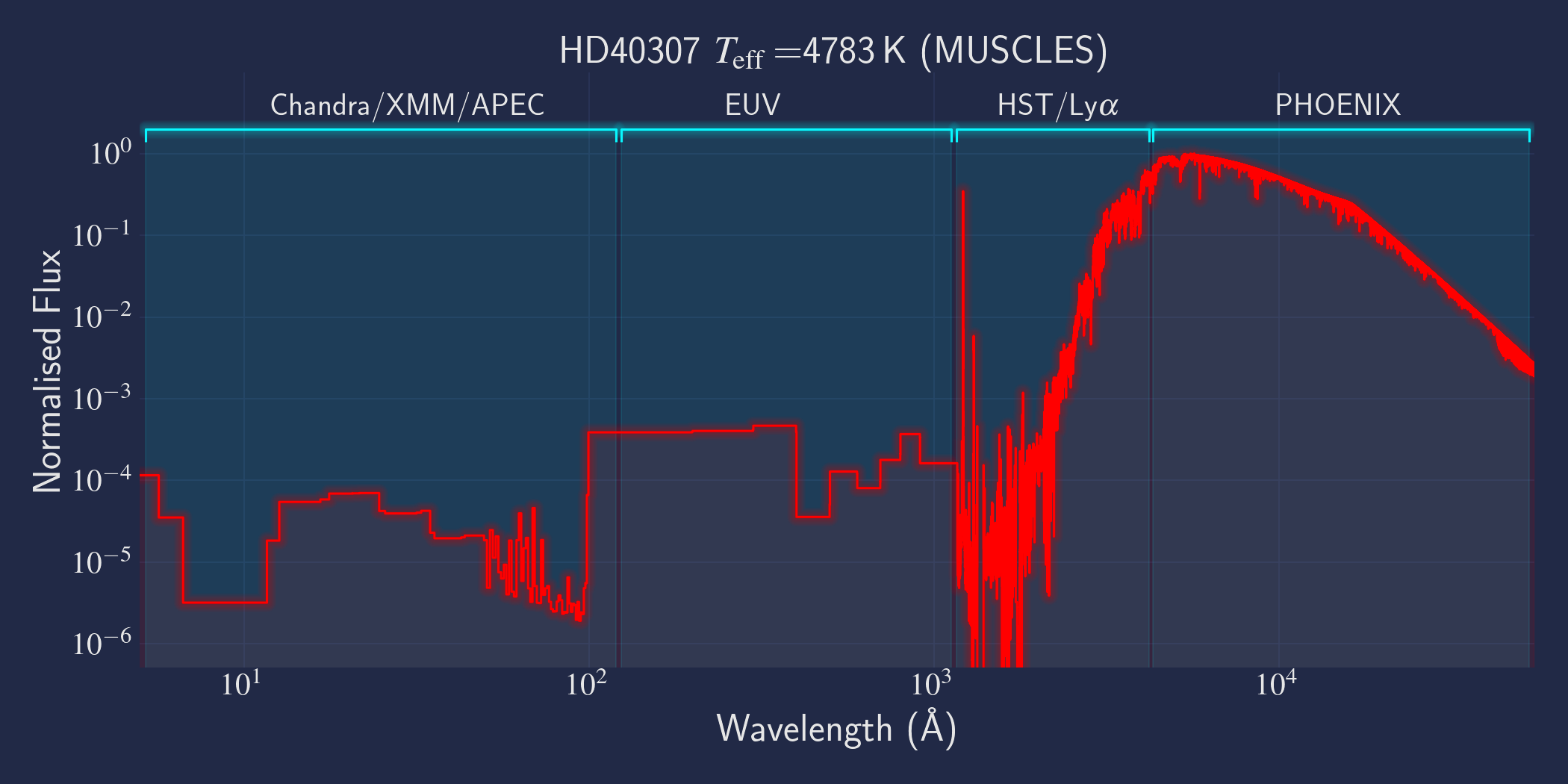
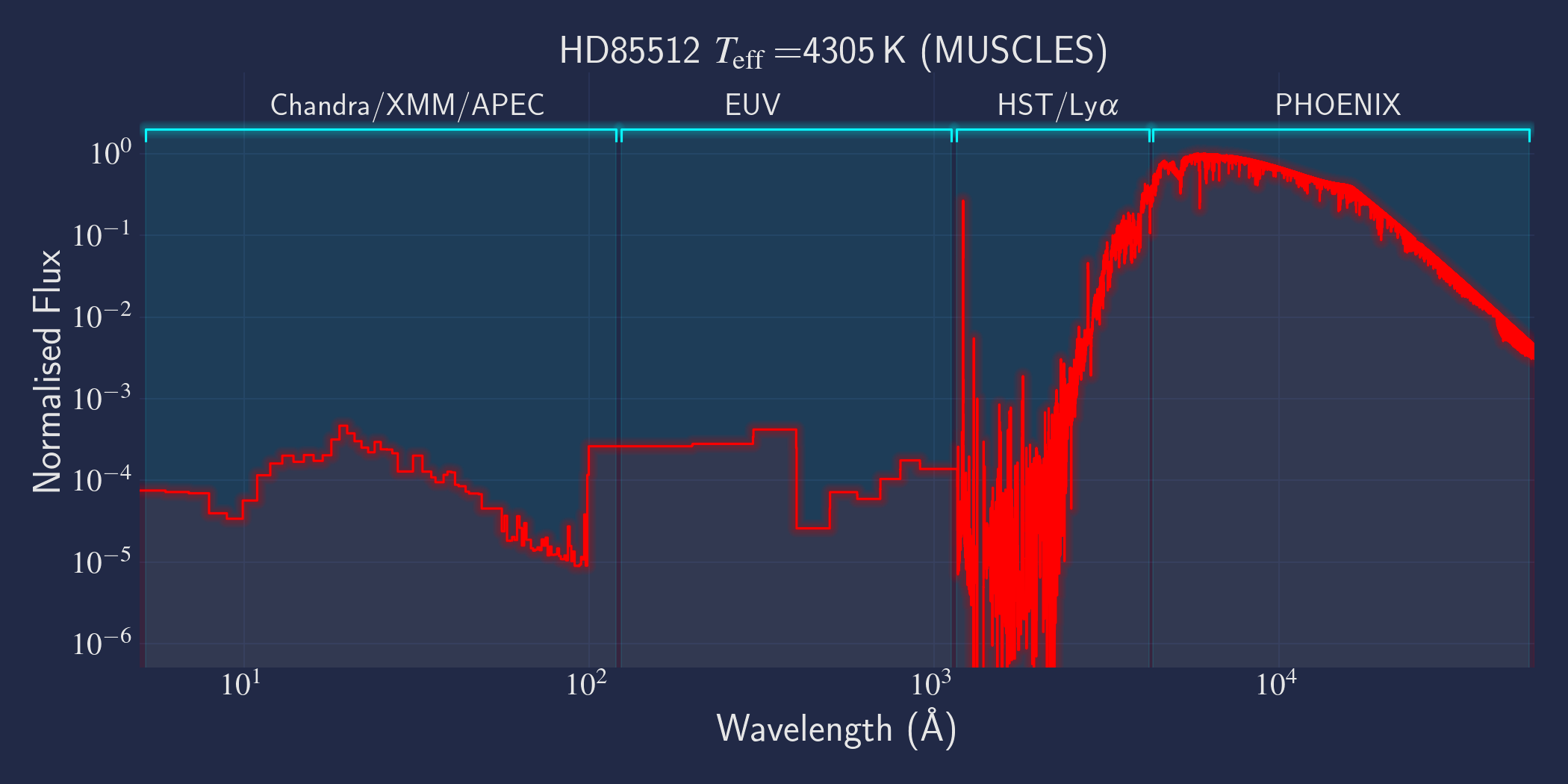
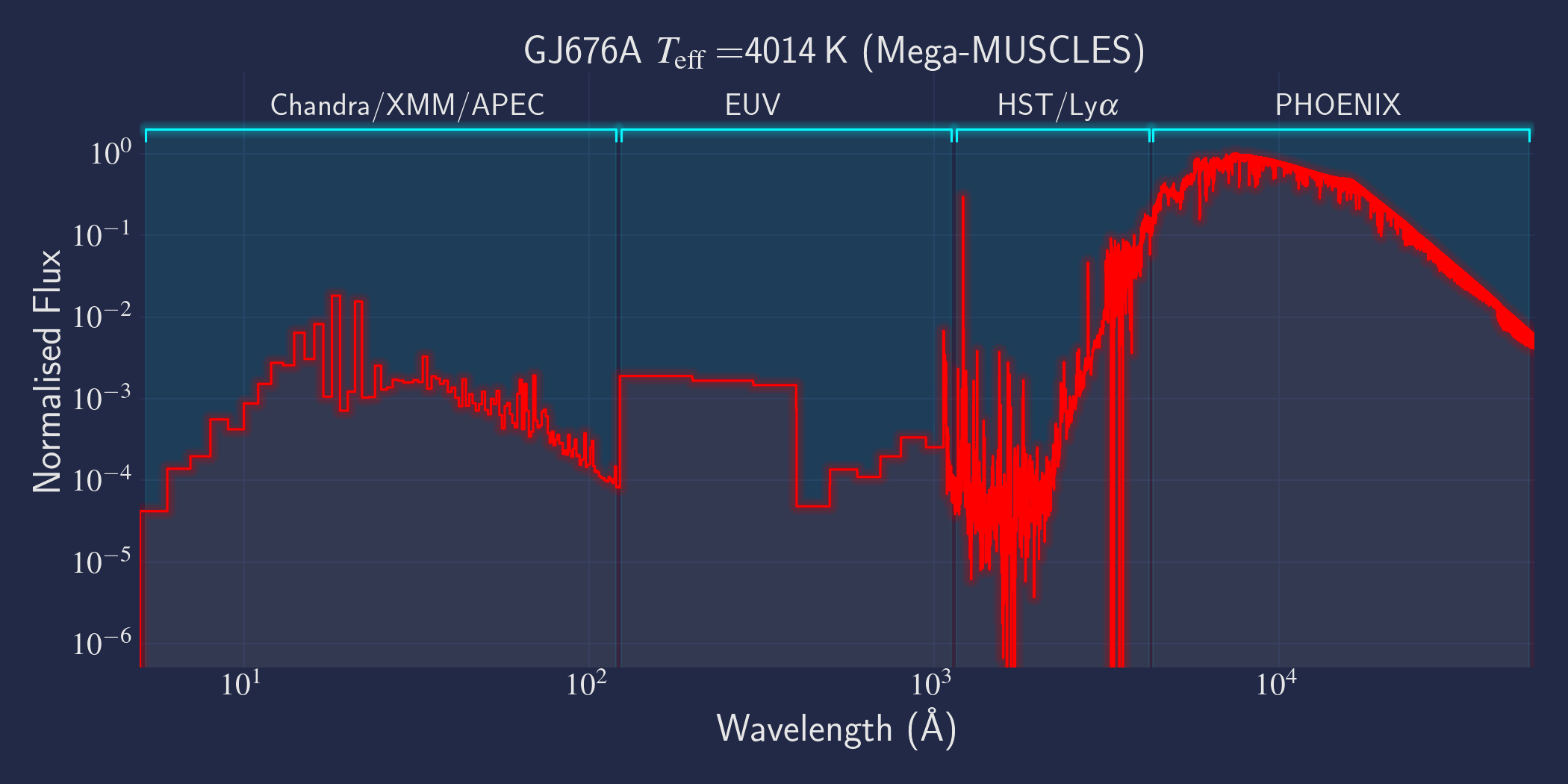
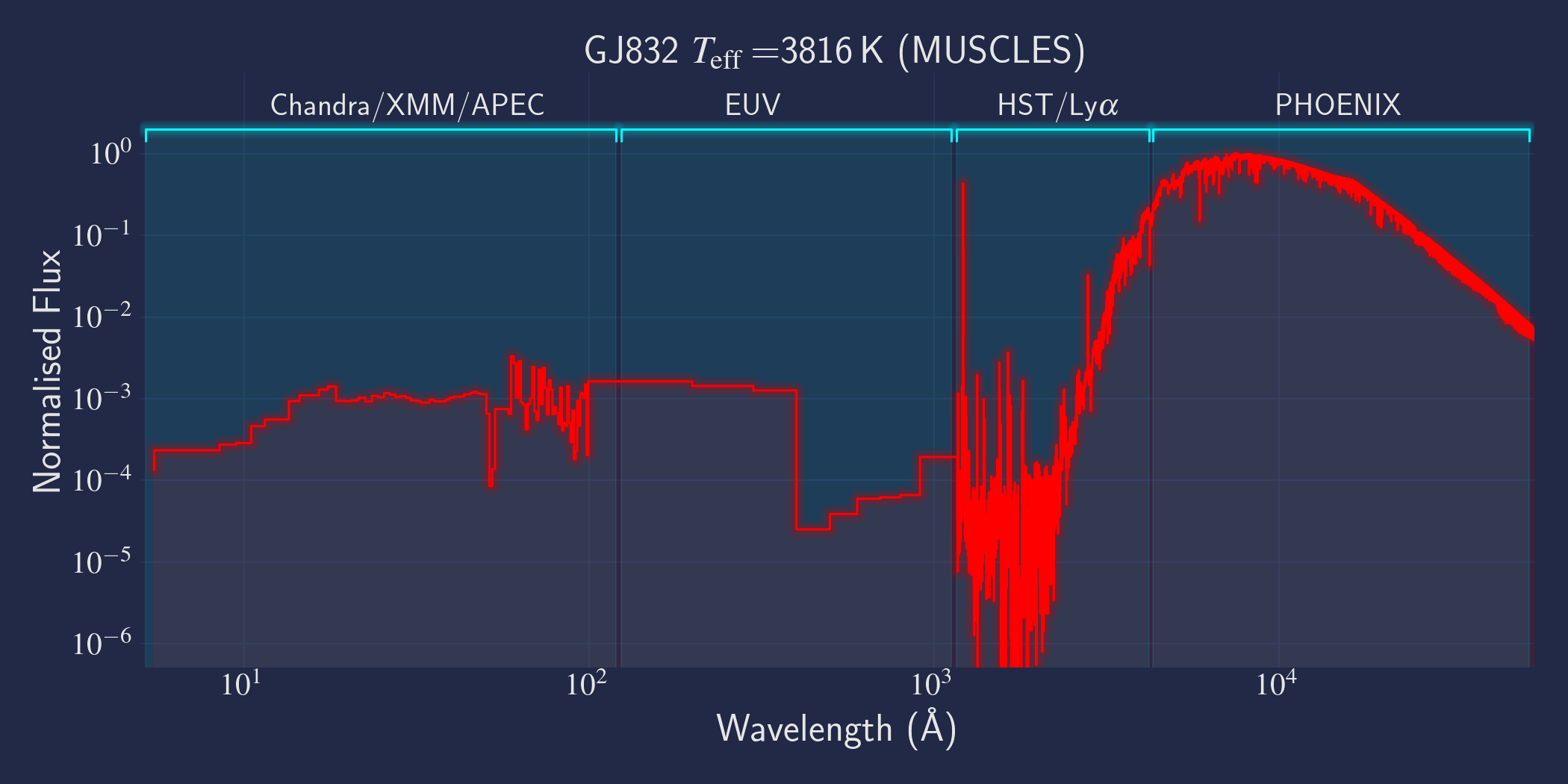
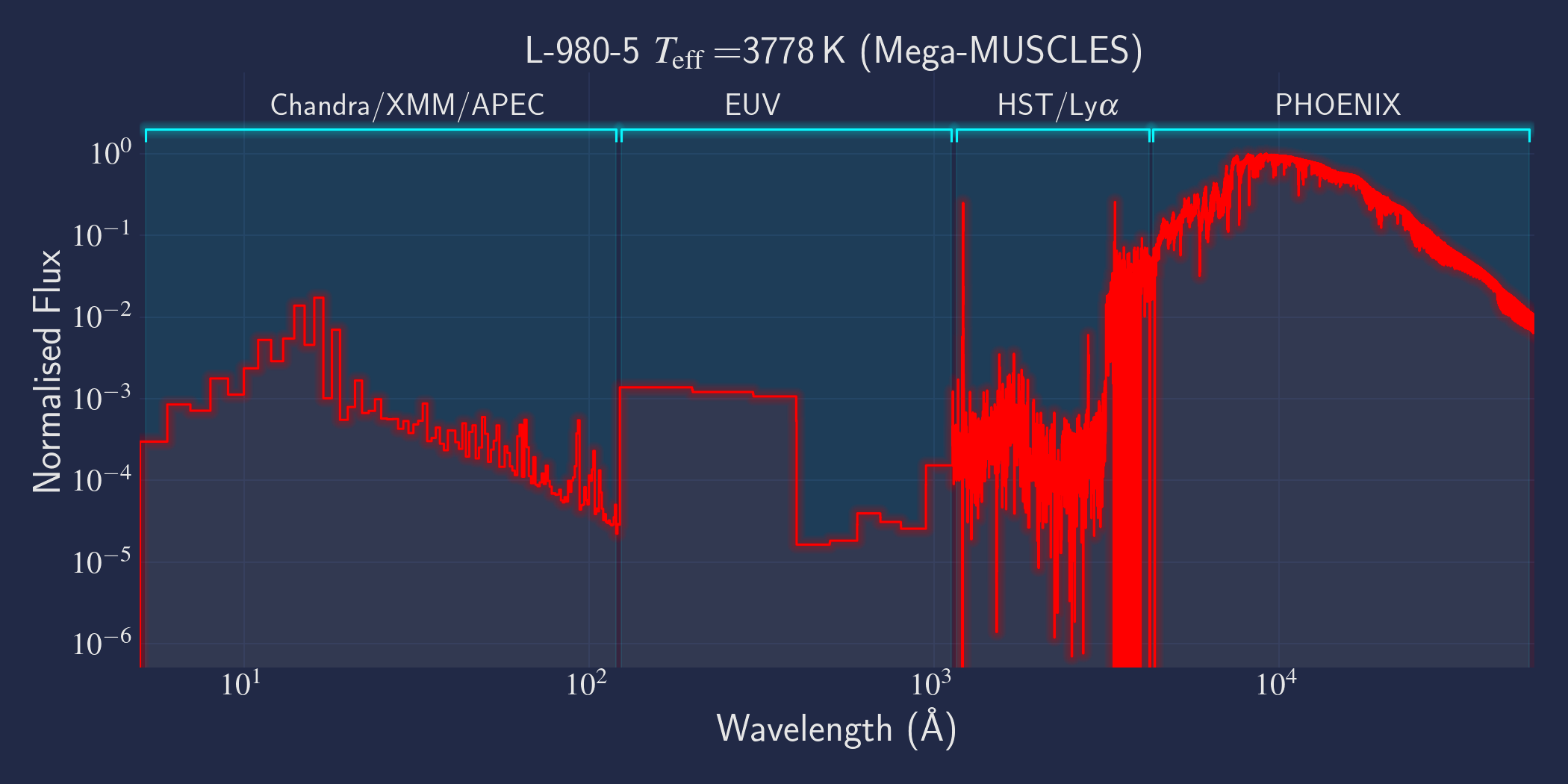
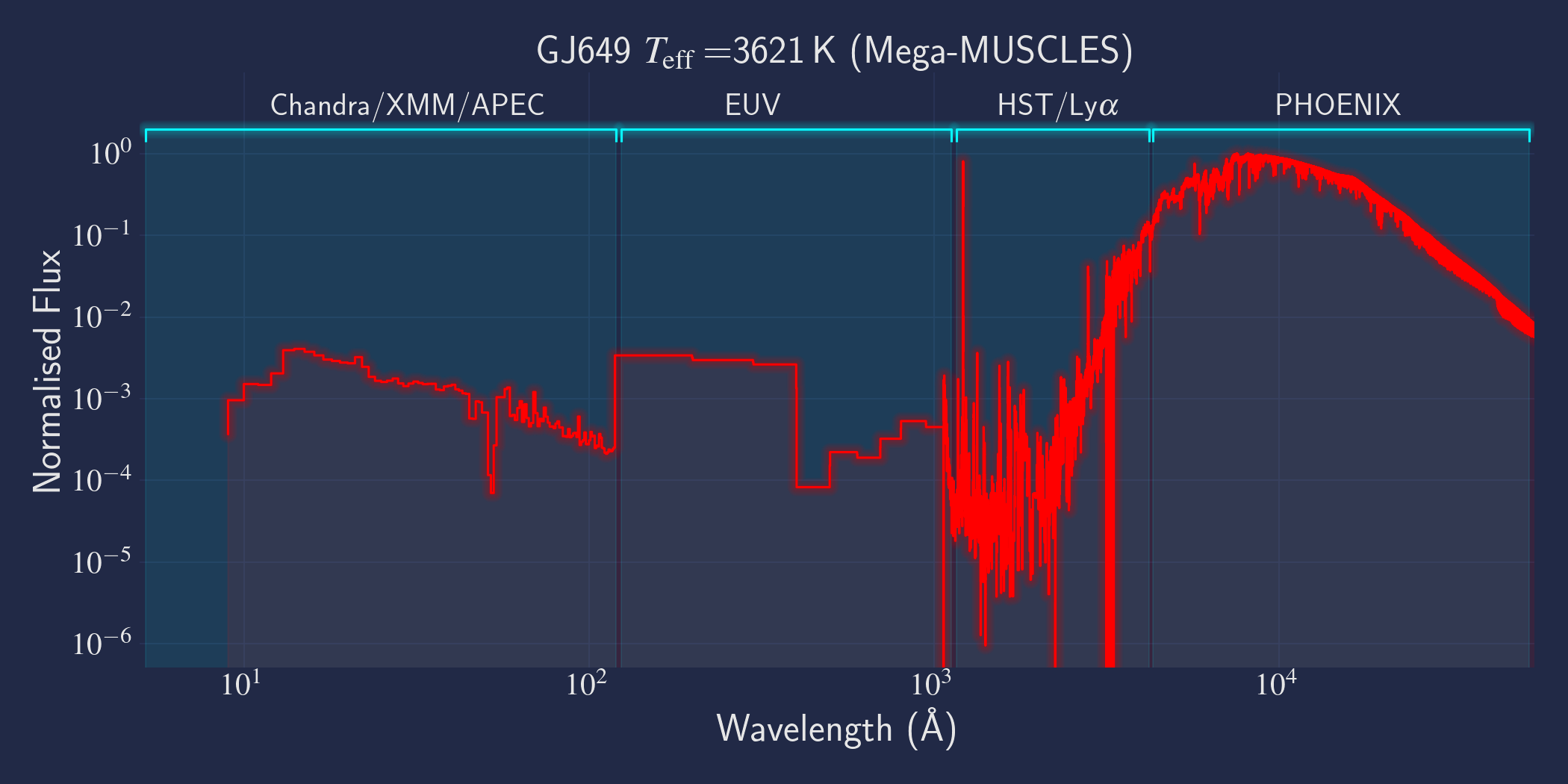
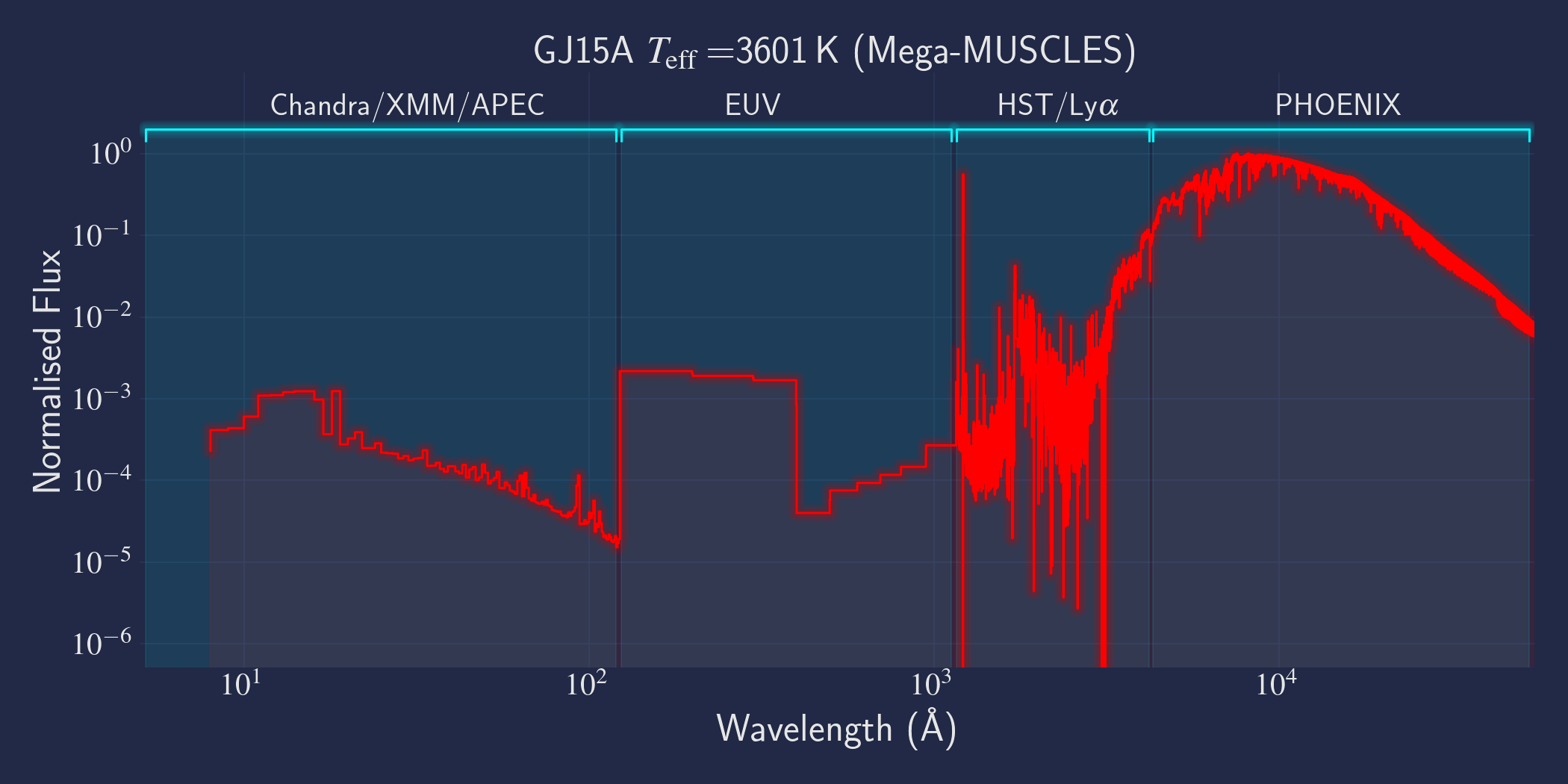
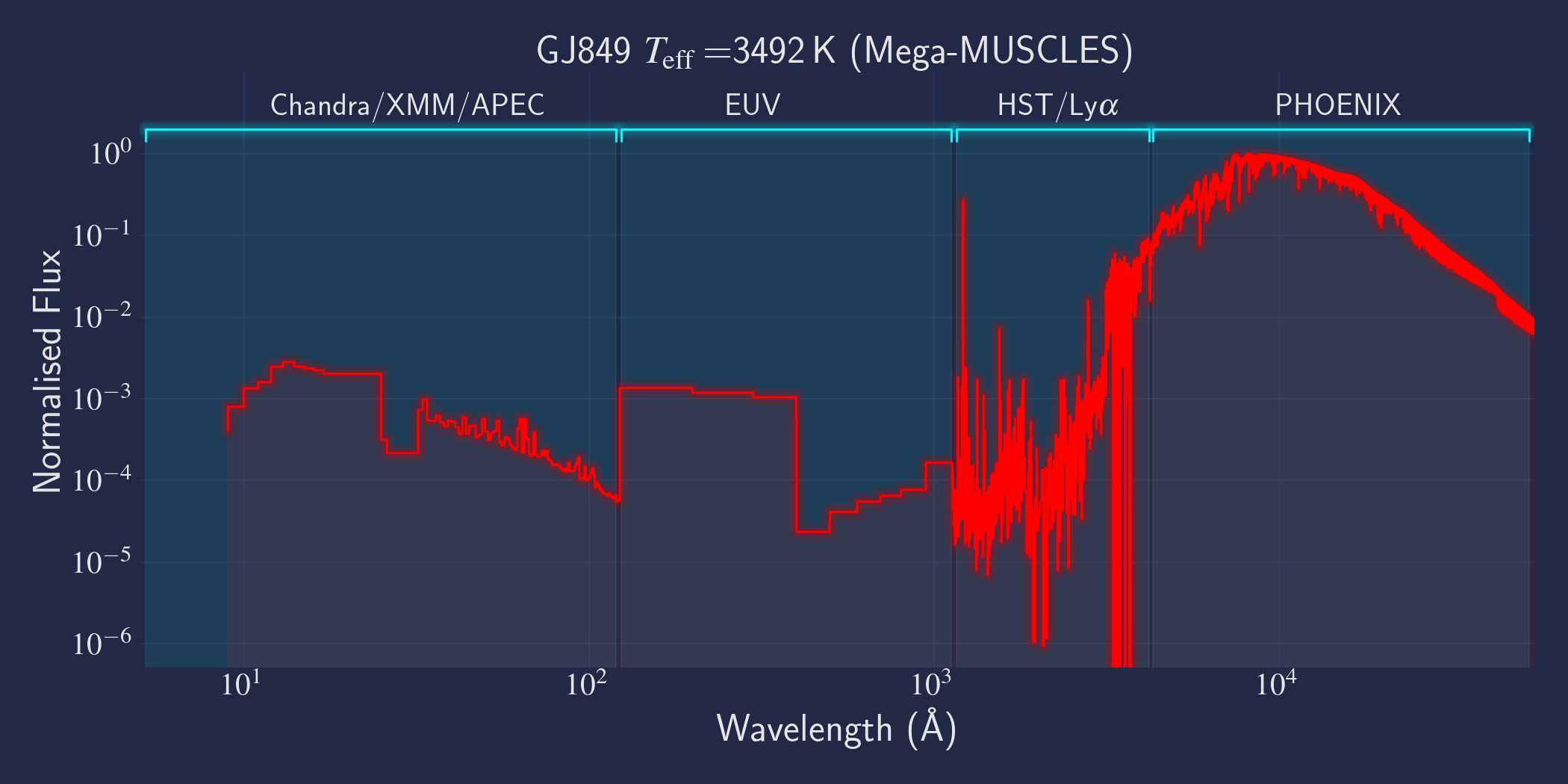
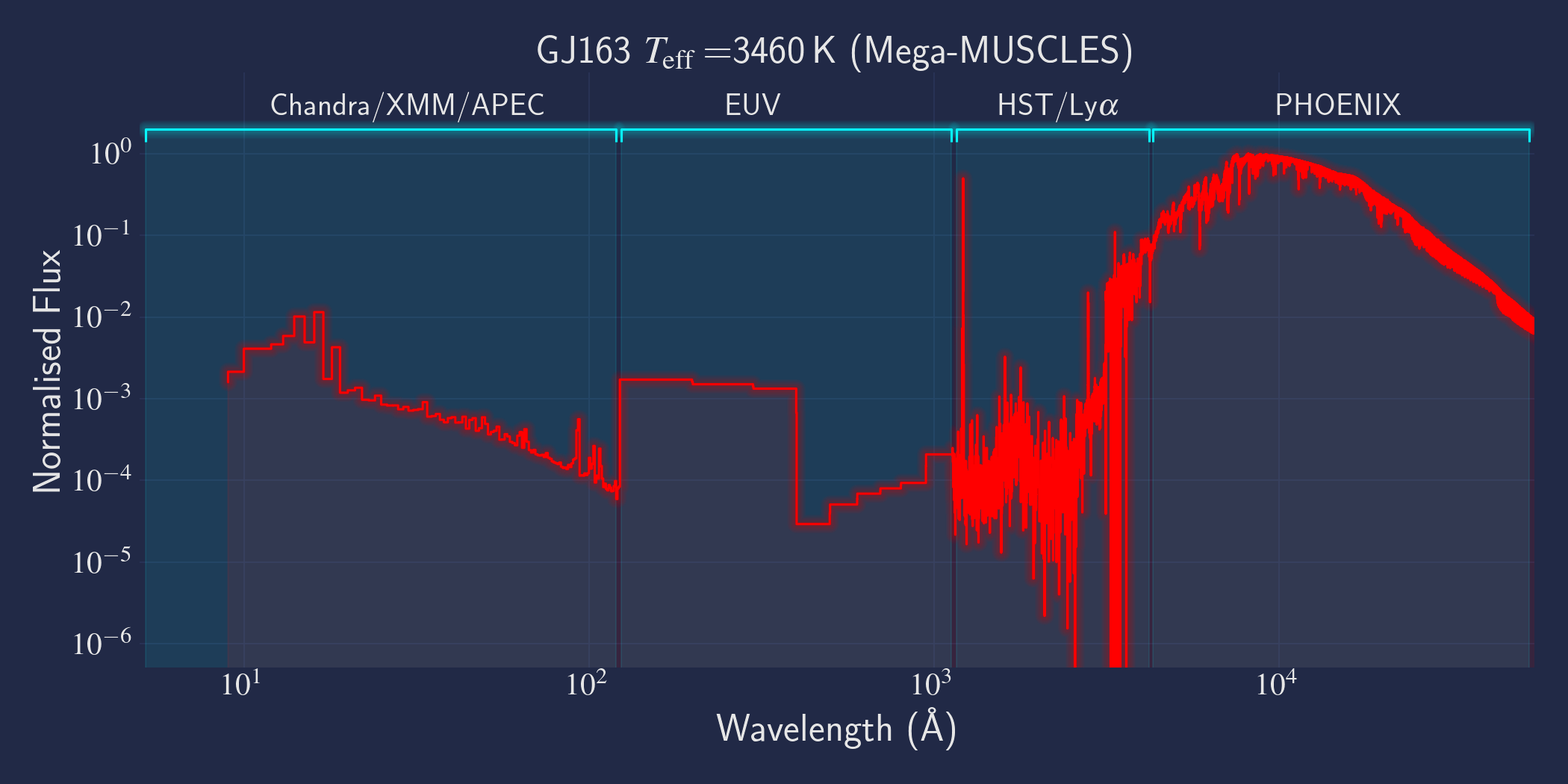
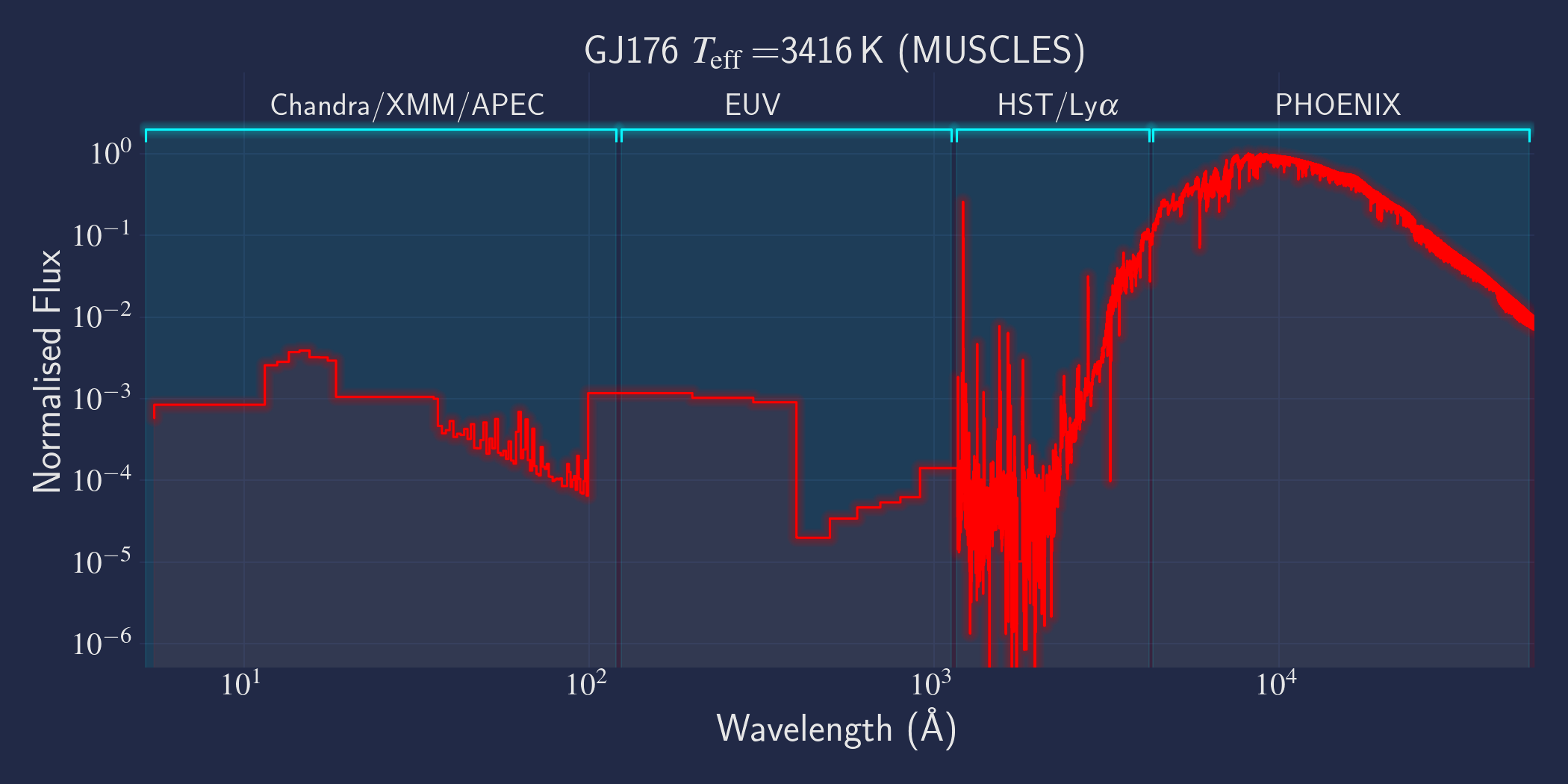
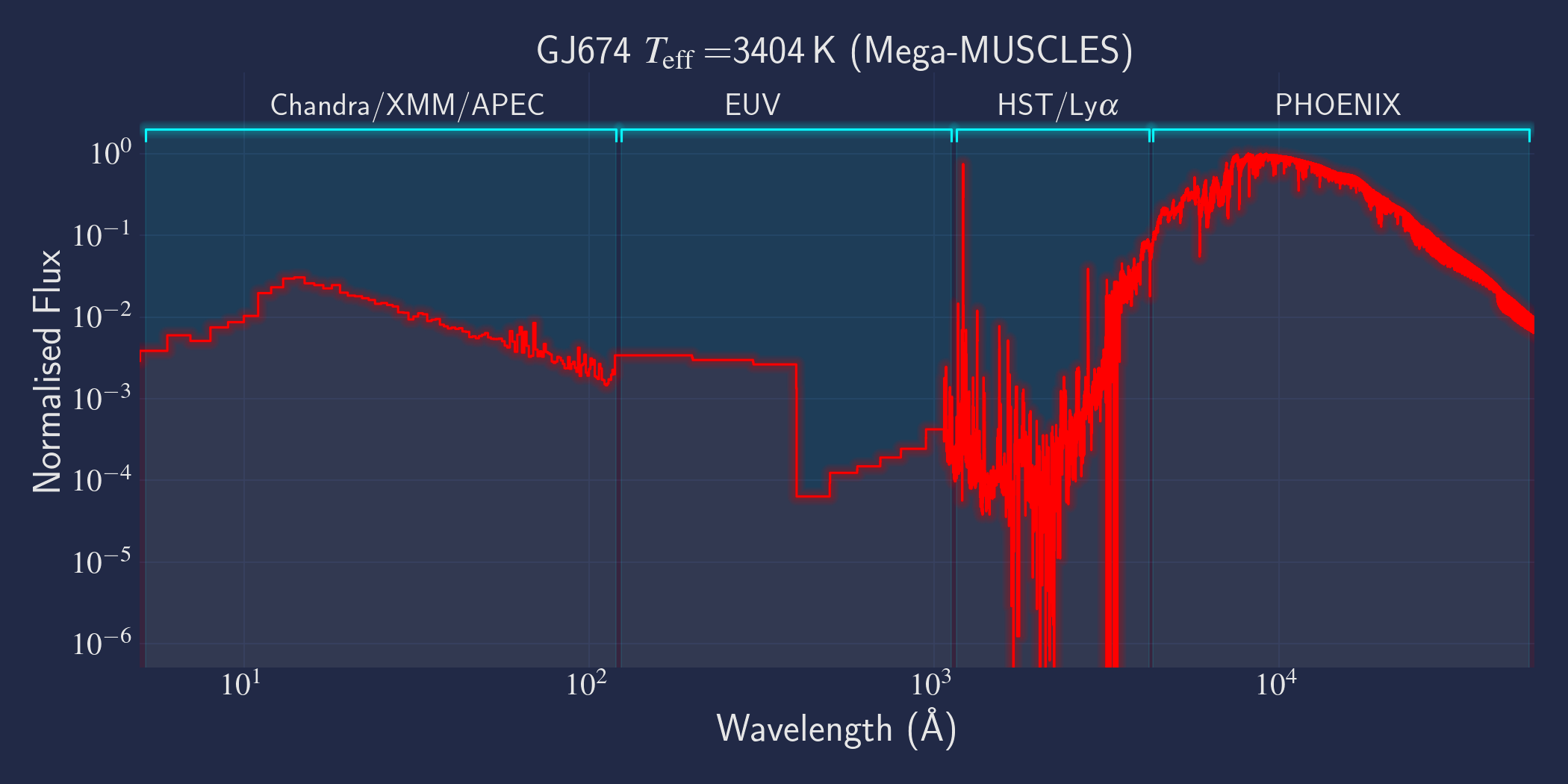
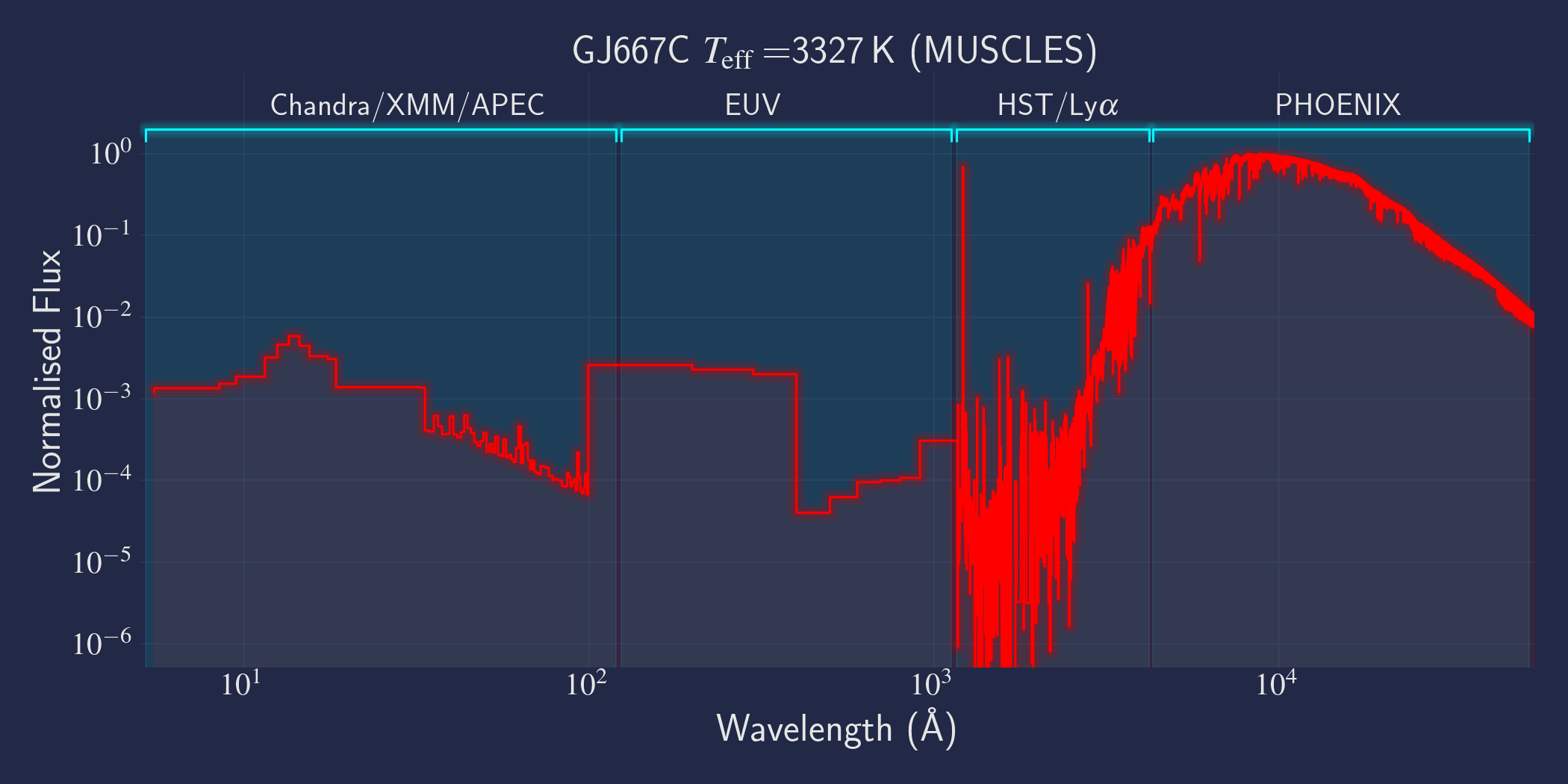
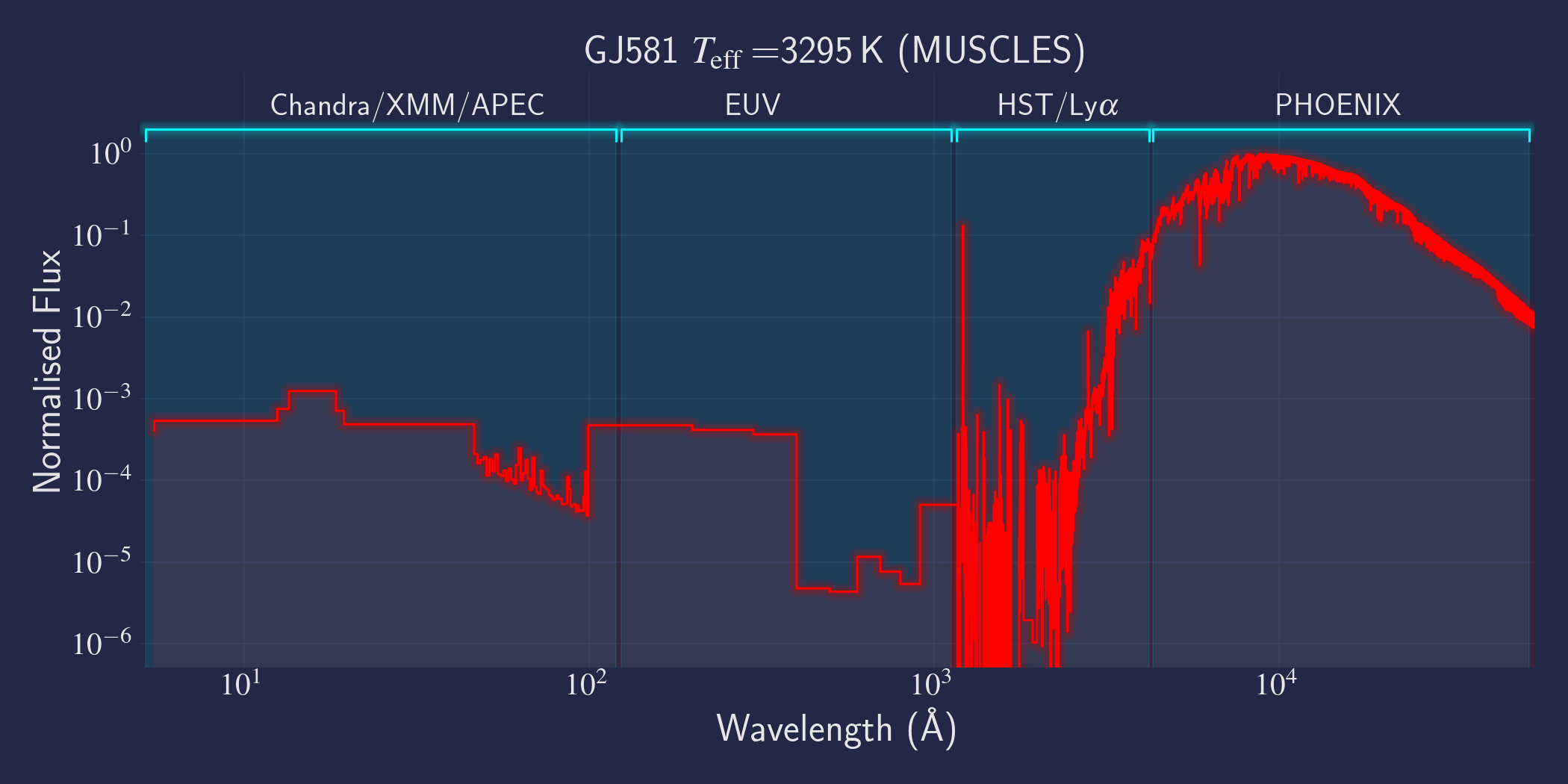
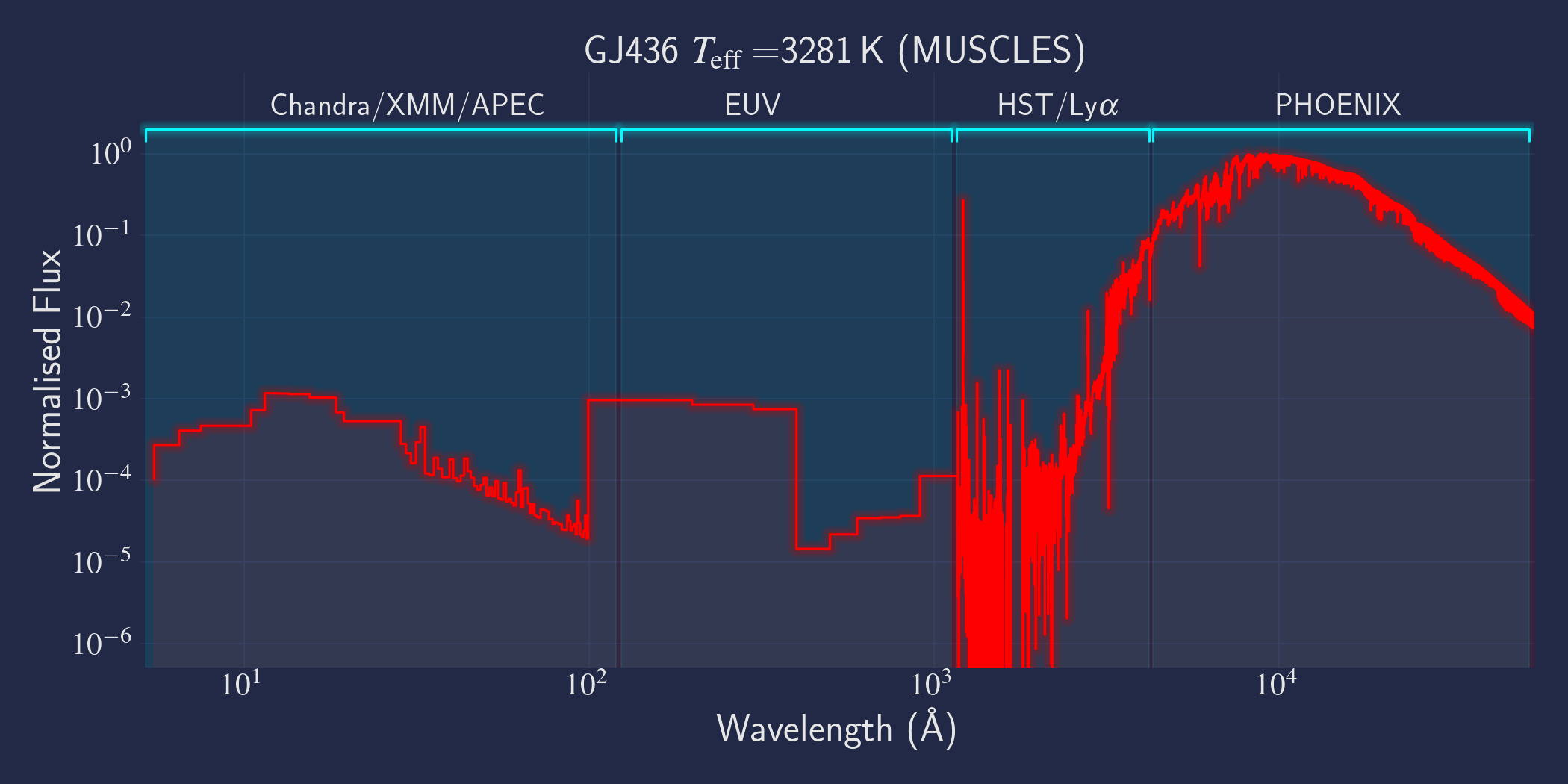
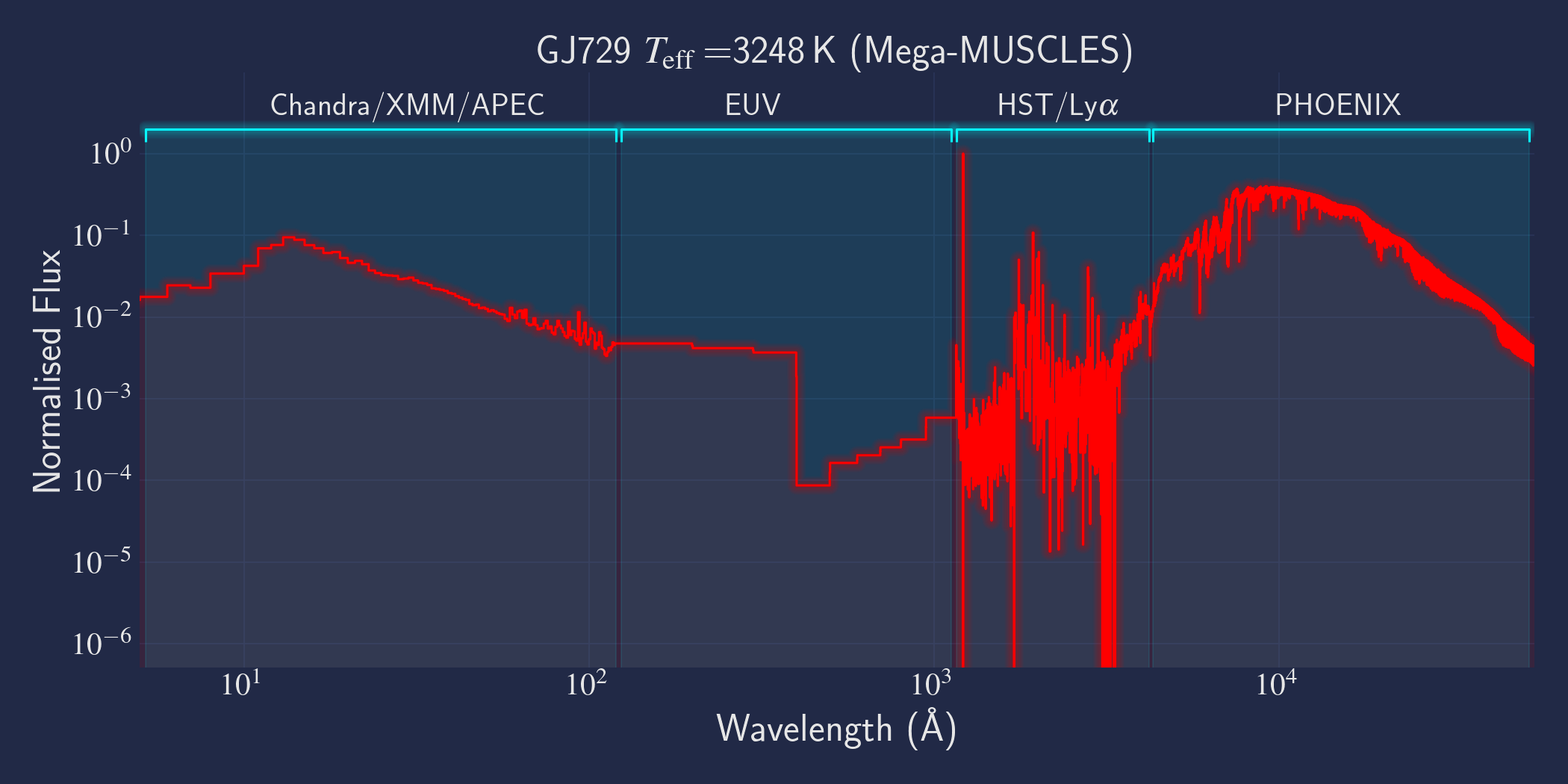
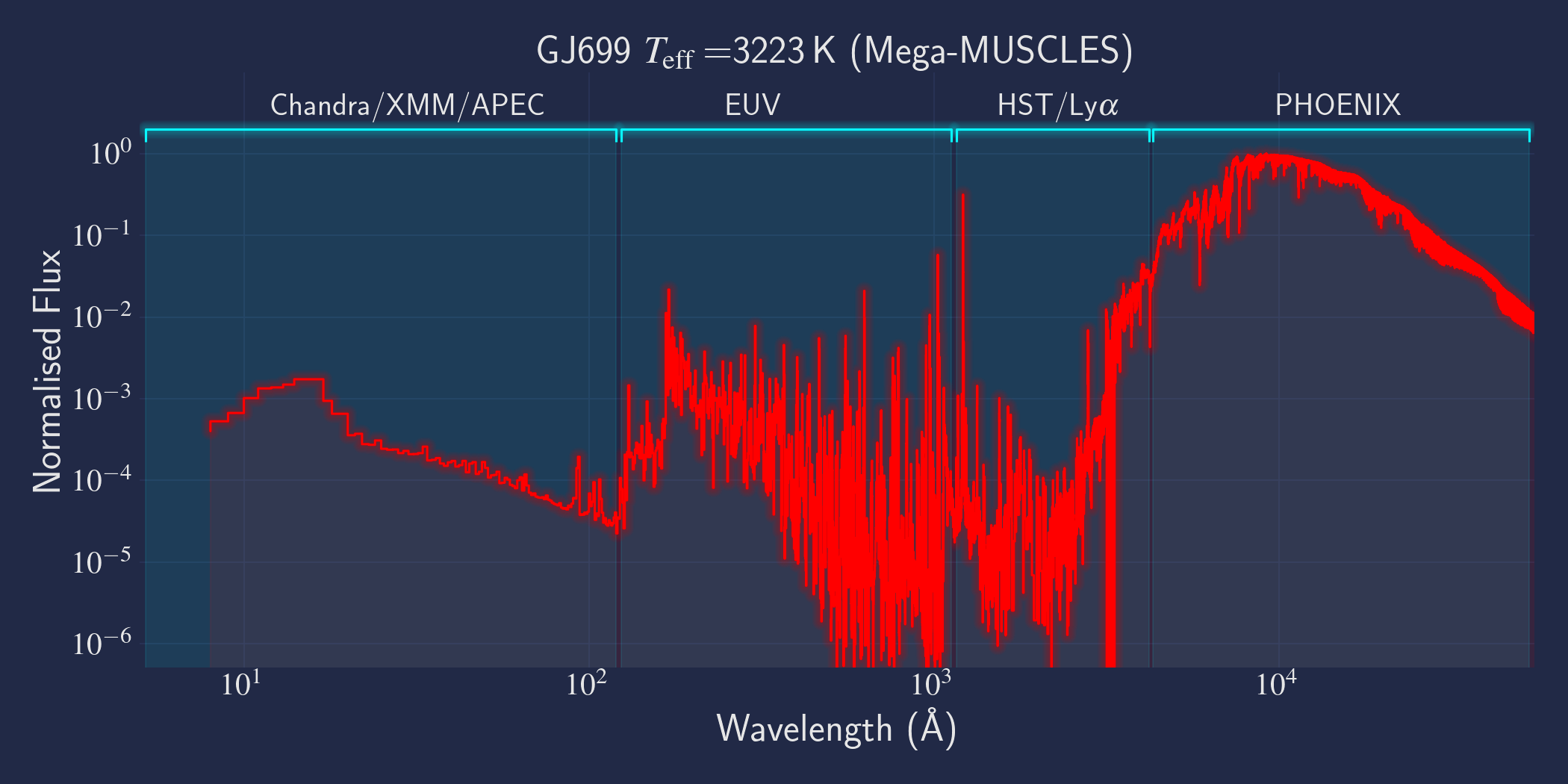
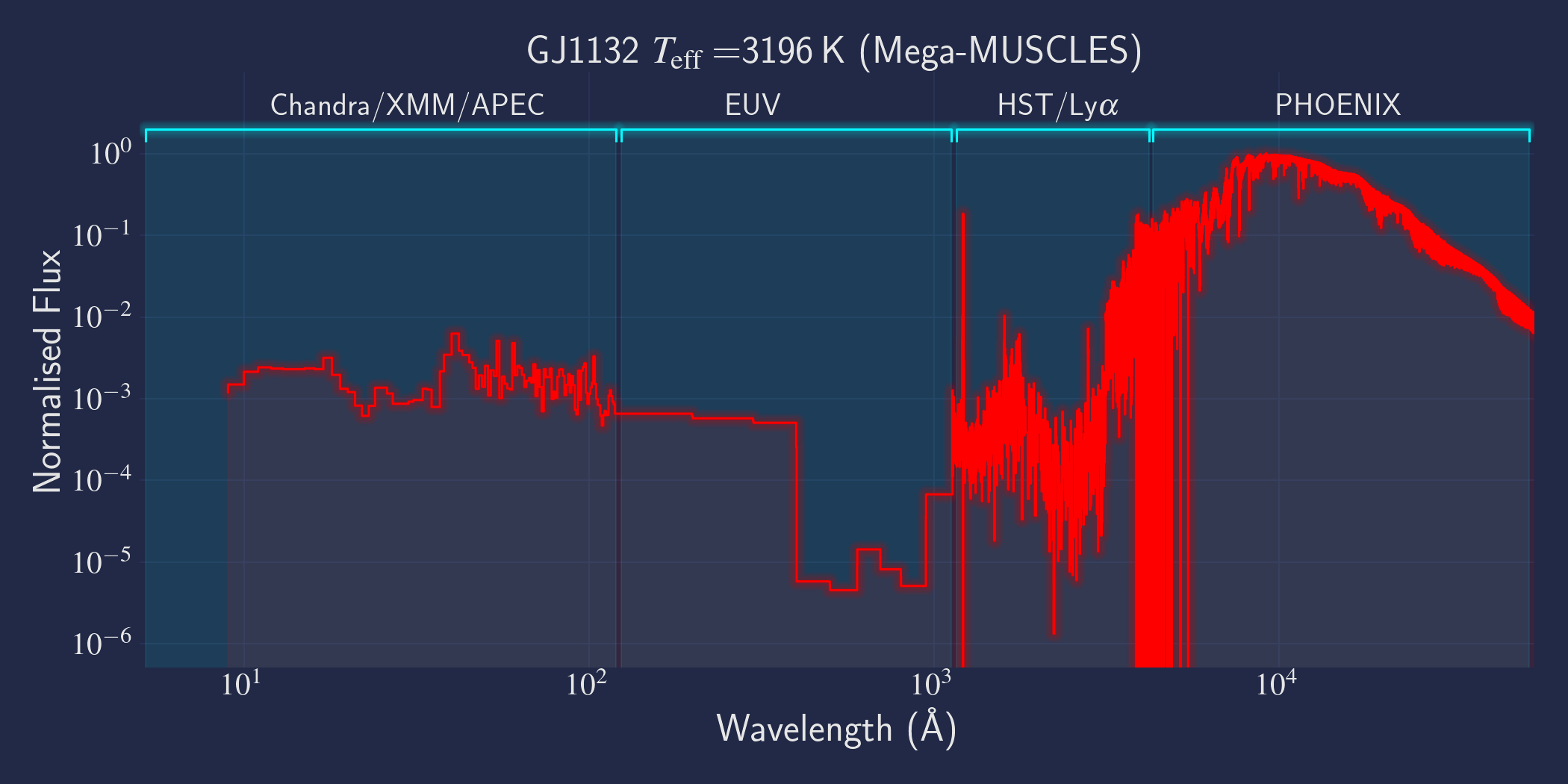
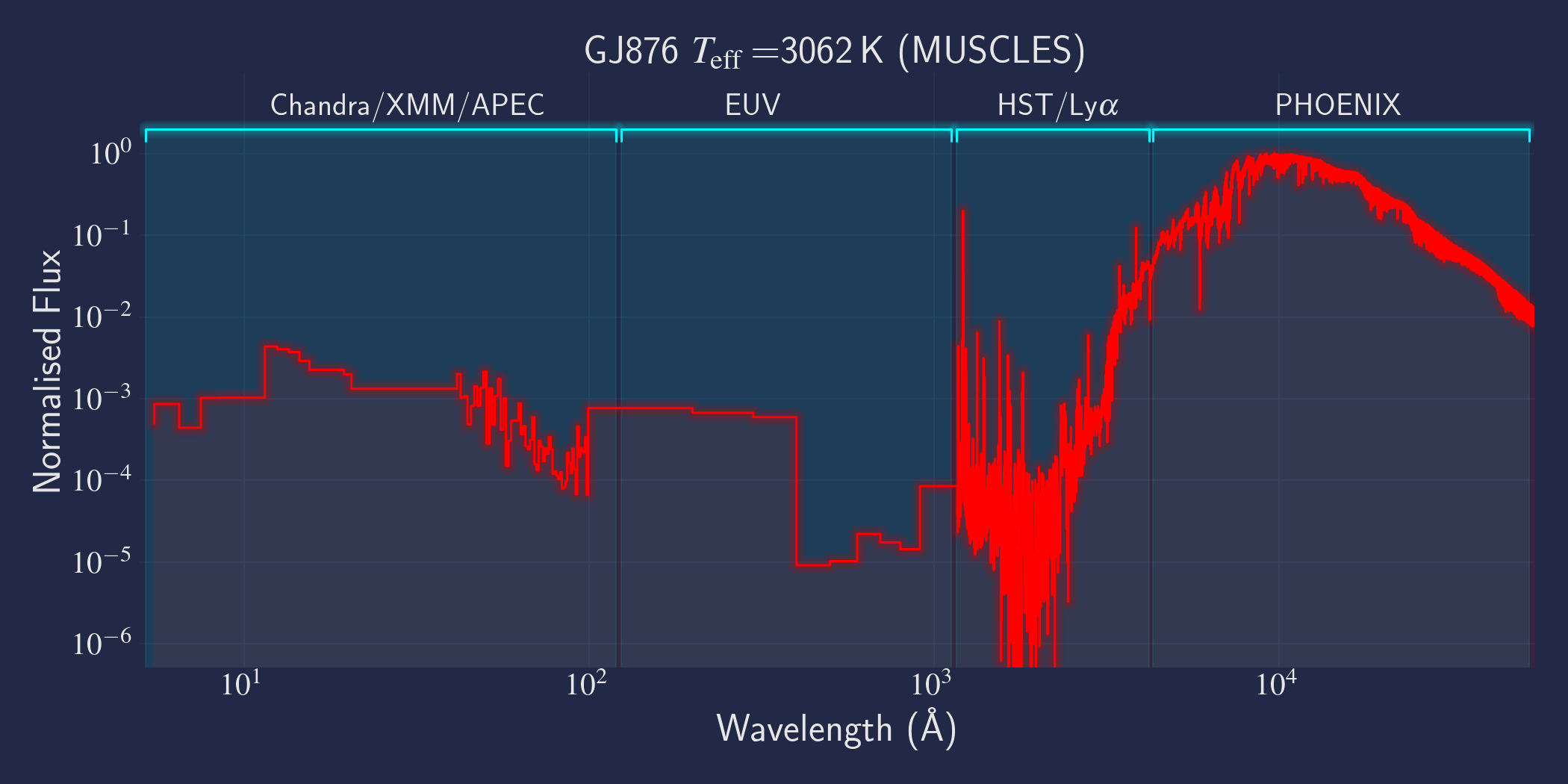
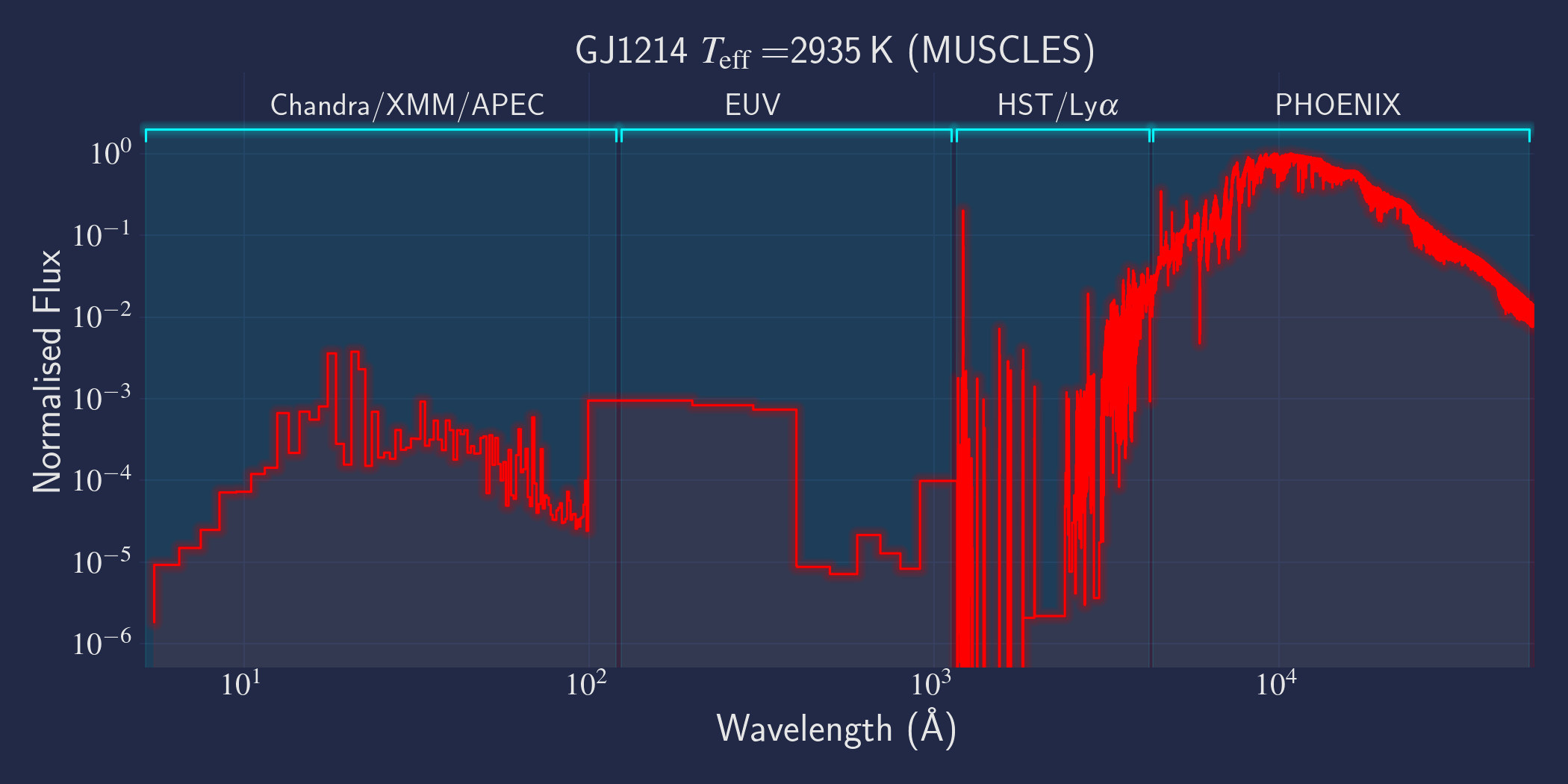
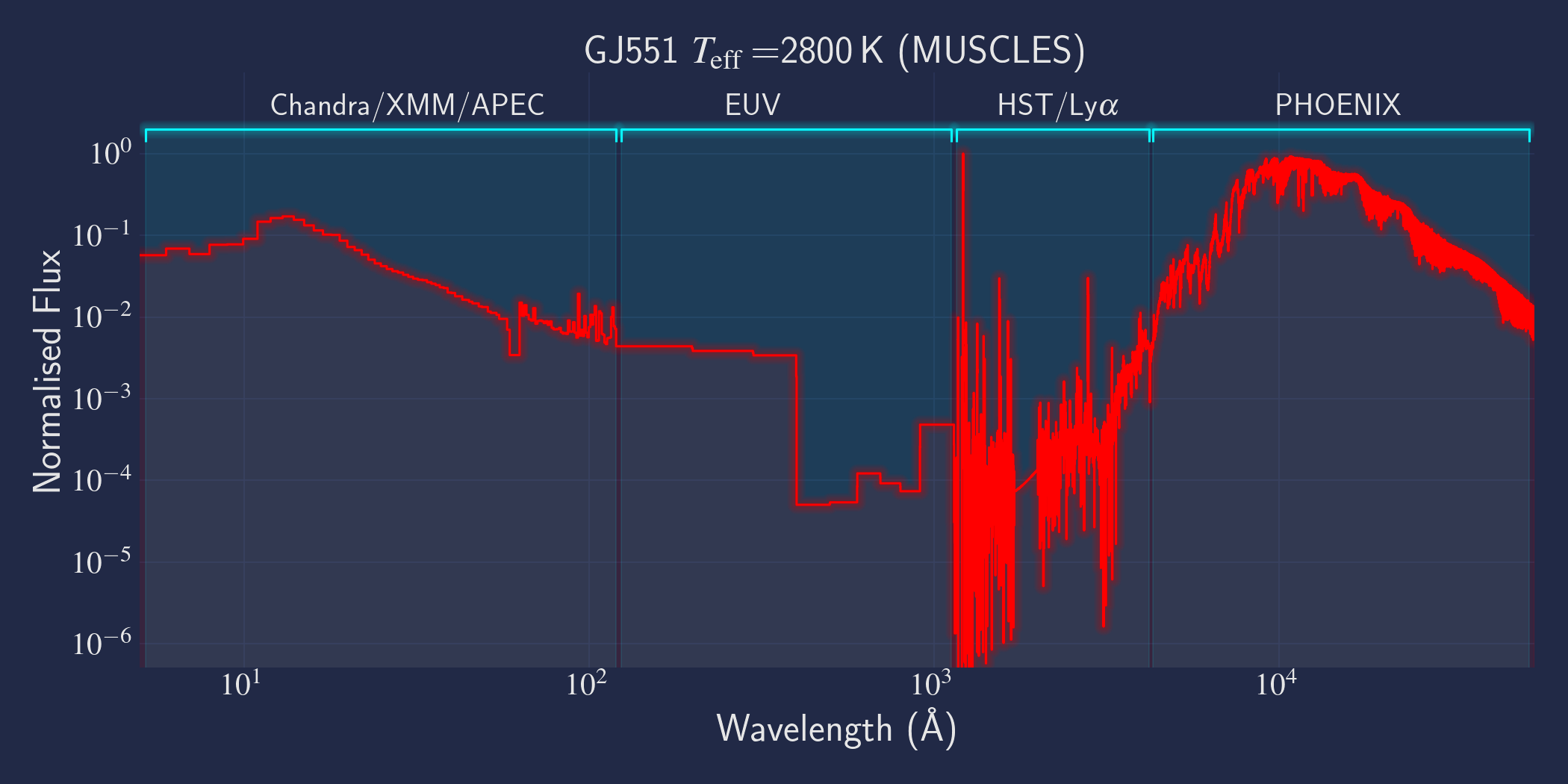
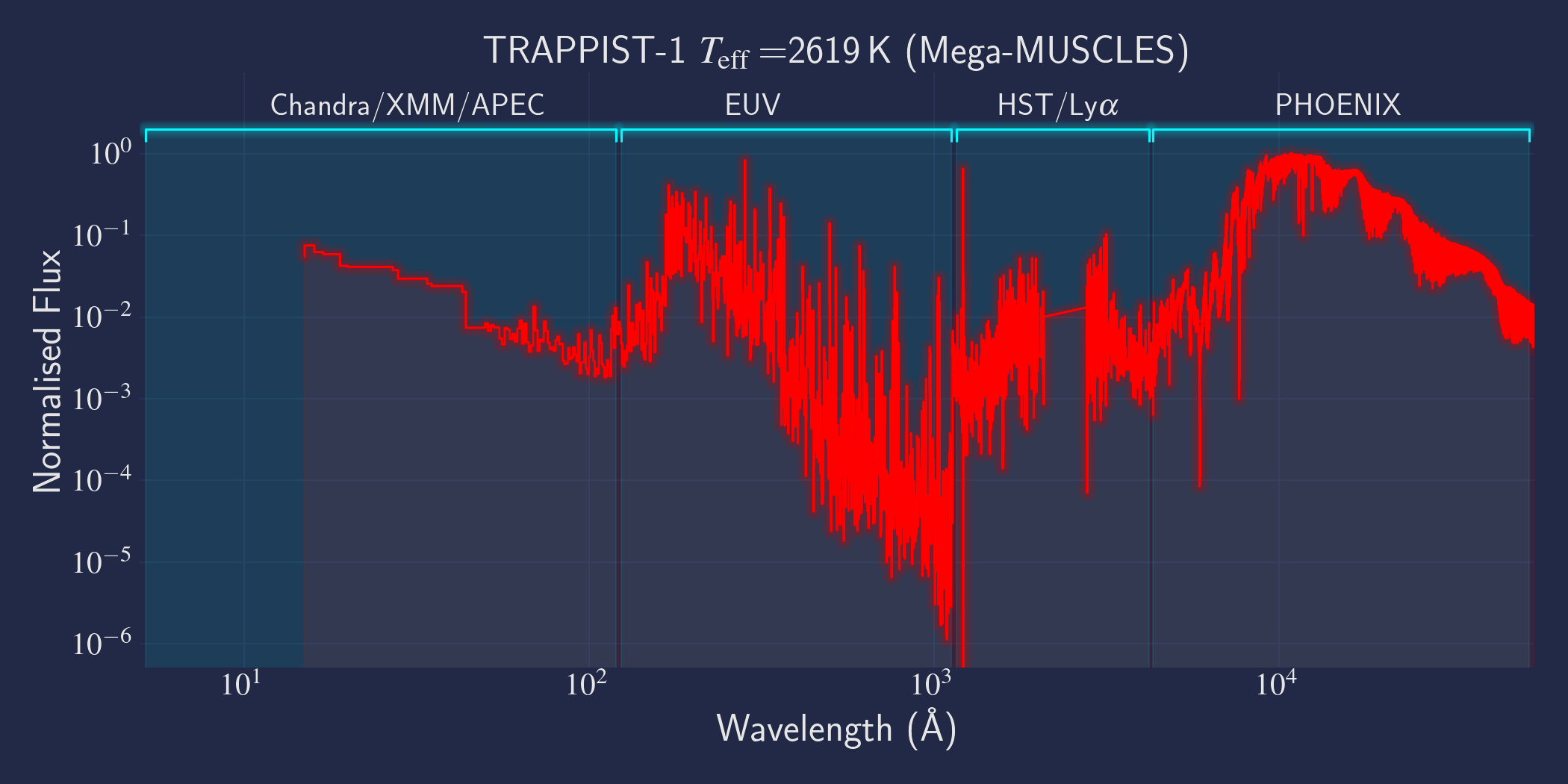
MUSCLES is a spectral survey of 11 low-mass, planet-hosting stars, 7 M and 4 K dwarfs. The follow-on Mega-MUSCLES survey observed 12 more M dwarfs, extending the spectral type coverage down to M8. The spectra cover wavelengths from 5 Å to 5.5 µm (MUSCLES) / 1000 µm (Mega-MUSCLES), with emphasis on high-energy radiation. More information on the MUSCLES survey and collaboration can be found at the MUSCLES team page. Data sources for the various regions of the spectra are:
- X-rays: Chandra/XMM-Newton/Swift and APEC models (Smith et al. 2001, ApJ, 556, 91)
- EUV: Empirical scaling relation based on Lya flux (Linsky et al. 2014, ApJ, 780, 61) and/or Differential Emission Measure models (Duvvuri et al. 2021, ApJ, 913, 40)
- Lya: Reconstructed from model fit to line wings (Youngblood et al., 2016, ApJ, 824, 101)
- FUV - blue visible:: HST COS and STIS
- Visible - IR: Synthetic photospheric spectra from PHOENIX atmosphere models (Husser et al. 2013, A&A, 553, 6 and Allard 2016)
Data Products
The data products from all stars are organized into subdirectories based on the star name. Several files are available for each target. We provide a brief summary below, for full details, consult the README file.
Primary Data Products
- *const-res-sed.fits = Panchromatic SED binned to a constant 1 Å resolution. One file per star.
- *var-res-sed.fits = Panchromatic SED that retains the native instrument resolutions where possible. One file per star.
- *adapt-const-res-sed.fits = Panchromatic SED binned to a constant 1 Å resolution, downsampled in low signal-to-noise regions to avoid negative fluxes. One file per star.
- *adapt-var-res-sed.fits = Panchromatic SED that retains the native instrument resolutions where possible, downsampled in low signal-to-noise regions to avoid negative fluxes. One file per star.
Ancillary Data Products
- *hst_cos*component-spec.fits = Coadded HST COS spectrum. One file per observed grating (three for each star, except V-EPS-ERI, which has two).
- *hst_stis*component-spec.fits = Coadded HST STIS spectrum. One file per observed grating (three for each star, except V-EPS-ERI, which has four).
- *euv-scaling*component-spec.fits = Extreme UV spectrum based on empirical scaling relation using Lyα flux. One file per star.
- *lya-reconstruction*component-spec.fits = Reconstructed spectrum from model fits to Lyα line profiles accounting for the stellar flux and the interstellar medium. One file per star.
- *phx*component-spec.fits = Synthetic spectrum in the visible and infrared from PHOENIX models. One file per star.
Proxima Centauri (GJ 551)
In response to popular demand after the announcement of the discovery of a habitable-zone planet orbiting Prox Cen, we added Prox Cen to the MUSCLES sample and created an SED from archival data using methodology consistent with the other MUSCLES SEDs. We highly encourage users of the Prox Cen spectra to read these notes on the reduction of the Prox Cen spectra, as they address an important issue regarding the stellar effective temperature and bolometric flux.
MUSCLES Extension (Jump To Data Access)
The MUSCLES Extension SEDs are similar to the MUSCLES SEDs and follow the same file naming conventions. The readme for the MUSCLES SEDs applies in all cases except where detailed below.\n Major differences between MUSCLES and MUSCLES Extension are as follows:
- FUV and X-ray proxy stars: Due to low signal to noise in FUV and X-ray observations, the MUSCLES Extension SEDs use scaled proxy stars of similar spectral type and age for these regions. The regions where proxy stars are used is typically 5 < λ < 100 Å and 1170 < λ < ~1900 Å. The end of the proxy spectrum varies from target-to-target depending on the S/N of the STIS G230L spectra.
- Flux Scalings: No adjustments have been made to the STIS flux calibration.
- PHOENIX models: MUSCLES Extension uses PHOENIX photospheric model spectra from the Lyon BT-Settl CIFIST 2011_2015 grid (Allard 2016). The models extend to 5.5 microns.
Semi-Empirical Models (Jump To Data Access)
Also available for download is a synthetic spectrum of the MUSCLES M2 dwarf GJ 832 from Fontenla et al. 2016. The synthetic spectrum was created from a one-dimensional model of the stellar atmosphere that incorporates non-LTE radiative transfer techniques and many molecular lines. The synthetic spectrum covers 1 Å - 1 mm at a resolving power R = 100,000 (denoted by "r1e5" in the file names). A single resolution element equals two wavelength samples. For consistency with the MUSCLES data products, the synthetic spectrum's wavelength is in Angstroms and the flux is reported as would be observed from Earth (erg/cm2/s/Å) under the assumption that the stellar radius = 0.499 R_solar (Houdebine 2010) and distance = 4.95 pc (van Leeuwen 2007). Note that Houdebine et al. 2016 determine GJ 832's stellar radius to be 0.458 ± 0.039 R_solar. The atomic and molecular transitions appear at their laboratory rest wavelengths (vacuum). Semi-empirical models of the other 10 MUSCLES stars as well as Proxima Centauri and TRAPPIST-1 are coming soon. If you utilize the GJ 832 synthetic spectrum, please cite Fontenla et al. 2016, ApJ, 830, 154.
Data Access
Click on a star name to visit the Simbad page for that target. Download a .tar.gz containing all FITS files for a target using the (tar) link. Click on "FITS" to directly download the FITS file. Click on "PL" to use the MAST interactive plotter.
Target's with a double asterisk (**) denote Mega-MUSCLES targets and should cite the Mega-MUSCLES papers when used in publications.
Note: The STIS observations used a few different modes for a given central wavelength, e.g., the _140_ column contains spectra observed with either the G140L, G140M, or E140M modes. The EUV column might include _euv-scaling_ and _dem_ spectra. In all cases, consult the FITS header and/or file name to get the full observation modes used for a given target.
NOTE: The X-ray spectrum for HD 97658 does not come from XMM or Chandra observations. It is scaled from X-ray data of HD 85512, which shows similar lines in the UV. For more details, consult the README or primary publication.
‡ NOTE: The links in the top row of the "_230_" cell are for the E230M data, while the links in the bottom row are for the E230H data.
✠ NOTE: The X-ray spectrum for L980-5 is based on the upper limit flux from a Chandra non-detection.
| Target | XRAY | EUV | FUV-NUV-VIS | MIR | FIR-SUBMM | ALL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-100 Å) | (100-912 Å) | (912 Å - 2.5 μm) | (2.5 - 500 μm) | (500 μm - 1 mm) | |||
| R = 100,000 | R = 100,000 | R = 100,000 | R = 100,000 | R = 100,000 | R = 100,000 | ||
| GJ 832 (tar) | FITS PL | FITS PL | FITS PL | FITS PL | FITS PL | FITS PL | |
Example Plot Scripts
The example file used here, hlsp_muscles_multi_multi_gj436_broadband_v10_adapt-const-res-sed.fits, can be downloaded by clicking the "FITS" link in the GJ 436 / Adaptive Res row under the Panchromatic / Const column.
Python:
from astropy.io import fits
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
spec = fits.getdata('hlsp_muscles_multi_multi_gj436_broadband_v10_adapt-const-res-sed.fits',1)
plt.plot(spec['WAVELENGTH'],spec['FLUX'])
plt.xlabel('Wavelength (Angstroms)')
plt.ylabel('Flux Density (erg/cm2/s/Ang)')
plt.show()
IDL:
data_436 = MRDFITS(path+'hlsp_muscles_multi_multi_gj436_broadband_v10_adapt-const-res-sed.fits',$
1,head_436)
wave = data_436.wavelength
flux = data_436.flux
error = data_436.error
plot, wave, flux, xs=1, ys=1, xr=[10,50000], yr=[0.001,10000]*1d-15,$
/ylog, /xlog, TITLE='GJ 436; MUSCLES Example',$
xtitle='Wavelength (Ang)', ytitle='Observed Flux Density (erg/cm2/s/Ang)',$
charsize=1.75
|
|
|




 Follow Us
Follow Us